Search Efficiency in HashSet vs TreeSet in Java
Name: Timi Fung
Date: 12-11-2025
Teacher: Engelbert Fellinger
1. Introduction
Efficient search is important when handling large datasets. Choosing a collection without understanding its internal structure can slow down operations. In Java, HashSet and TreeSet are common implementations of the Set interface, but they work differently internally. Understanding these differences helps developers choose the right collection. This study focuses on search operations because they are frequently used in our Election project.
Main Research Question:
- Which Java collection, HashSet or TreeSet, provides faster search performance for large datasets?
Subquestions:
- How does TreeSet handle search operations internally?
- How does HashSet handle search operations internally?
- What are the practical differences in search time and memory usage between HashSet and TreeSet?
2. Definitions
A data structure organizes and stores data for efficient access and modification. An algorithm is a set of steps for solving a problem. In this context, the algorithms in HashSet and TreeSet determine how elements are stored and searched efficiently.
Time complexity measures how operation time grows with dataset size. Constant time complexity (O(1)) means the operation takes roughly the same time regardless of size. Logarithmic time complexity (O(log n)) grows slowly compared to linear time. Space complexity refers to the memory needed to store data.
A Set in Java is a collection of unique elements. HashSet stores elements without order and is optimized for fast searches. TreeSet keeps elements sorted, which is useful for ordered data or range queries, though searches are slightly slower than HashSet.
3. How TreeSet Handles Search Operations
TreeSet uses a Red-Black Tree internally, a self-balancing binary search tree. Elements smaller than a node go left, larger elements go right. Nodes are colored red or black, with the root always black. Insertions and deletions adjust colors and rotate nodes to maintain balance.
- If the Uncle is red than Recoloring is performed: parent and uncle become black, grandparent becomes red. This may propagate upward if the grandparent now violates the rules.
- If the Uncle is black or nill than Rotations (single or double) combined with recoloring restore the Red-Black properties. The type of rotation depends on the position of the new node relative to parent and grandparent: left-left, left-right, right-left, or right-right.
These rules ensures search, insertion, and deletion operations take O(log n) time. Searching traverses the tree in order. Space complexity is O(n), including nodes, links, and color information.
4. How HashSet Handles Search Operations
HashSet uses a HashMap internally. Each element is stored in a bucket based on its hash code. Collisions occur when multiple elements share a hash code; these elements are stored in a linked list. From Java 8 onwards, large buckets are converted to Red-Black Trees for efficiency.
Search, insertion, and deletion operations in HashSet are O(1) on average, but worst-case can be O(n) with extreme collisions. Memory usage is O(n), depending on the number of elements and buckets.
5. Code / Measurements
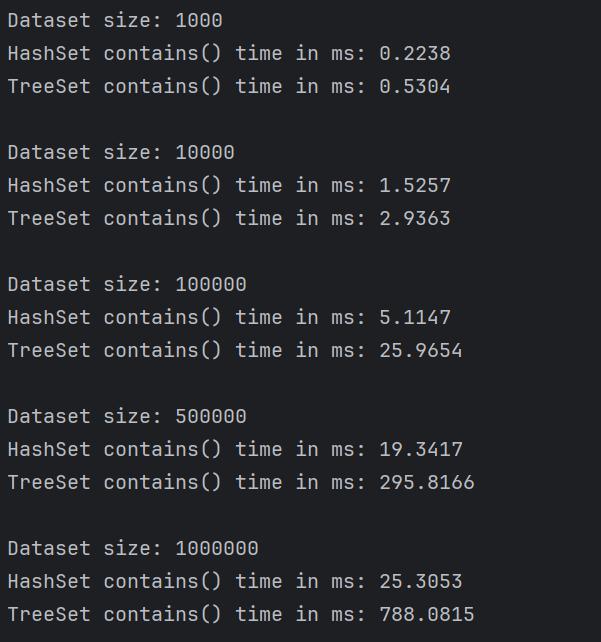
Measurements show HashSet search times remain almost constant as datasets grow, while TreeSet search times increase noticeably with larger datasets.
6. Conclusion
HashSet is faster for search operations, maintaining near-constant lookup times regardless of dataset size, consistent with its O(1) average-case complexity. TreeSet is slower but keeps elements sorted, which is useful for ordered data and range queries, following the expected O(log n) performance.
In summary, HashSet is best when search speed is the priority. TreeSet is more suitable when maintaining sorted order or performing range operations is important.
7. Sources
- RobEdwards. (2016, November 10). Red Black Trees 2 Example of building a tree [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v6eDztNiJwo
- UMBC CMSC 341 RBTDiagrams. (2007). Red-Black tree rotations. https://courses.cs.umbc.edu/undergraduate/341/Lectures/RedBlack/RBTDiagrams.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com
- Yusuf, A. D., Abdullahi, S., Boukar, M. M., Yusuf, S. I., Nigerian Communications Commission, & Department of Computer Science, Nile University of Nigeria. (2021). Collision Resolution Techniques in Hash Table: A Review. International Journal Of Advanced Computer Science And Applications, 12(9). https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/0f86/2e2bd5a40b6fa3442ed3005efb3b3aa8cdc0.pdf